Beyond the Buzzwords: Why New Interoperability Indices Are Your Blueprint for Digital Health Strategy
Interoperability. It's a foundational concept in digital health, but what does progress actually look like? The Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC) recently introduced a new set of indices to measure interoperability among U.S. hospitals, moving beyond simple "yes/no" questions to a more nuanced, measurable framework. For those of us in the digital health, virtual care, and direct care delivery space, this isn't just another government report—it's a critical blueprint for understanding the market, identifying opportunities, and building a sustainable business.
What the New Indices Tell Us
The new framework distills complex data exchange into three simple metrics:
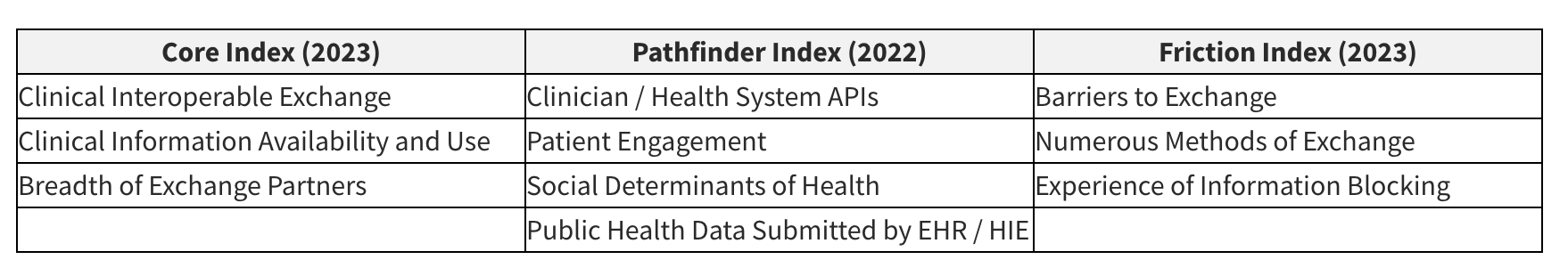
Core Index: This measures a hospital's adoption of foundational capabilities—the basics of clinical information exchange (Strawley & Everson, 2025). Think of it as a hospital's ability to send and receive patient summaries or clinical documents. A high score here signals a strong base for basic integration.
Pathfinder Index: This is where things get interesting for innovators. The Pathfinder Index measures the adoption of advanced technologies like FHIR®-based APIs, and a hospital's engagement with auxiliary exchanges (Strawley & Everson, 2025). A high score on this index means a hospital is technologically ready to integrate with next-generation digital health tools, including remote patient monitoring platforms, patient-facing apps, and advanced analytics.
Friction Index: This quantifies the barriers to interoperability, such as information blocking and the need to use numerous, disparate methods for data exchange (Strawley & Everson, 2025). This metric is a gut check on the real-world challenges of data liquidity. A high friction score is a warning sign that even with a strong technical foundation, data flow could be a significant obstacle.
The "So What" for Your Business
While these indices measure hospitals, they are a powerful tool for your business strategy. They provide a data-driven way to answer key questions about your target market.
1. Market Entry and Prioritization: The data reveals a significant digital divide. Smaller hospitals, critical access hospitals, and those in non-metropolitan areas perform significantly worse on the Core and Pathfinder Indices (Strawley & Everson, 2025). This is a vital piece of information. It tells you that a "one-size-fits-all" integration strategy won't work. When planning your market entry, you can use this data to prioritize:
Go-to-market strategy for larger hospitals: These facilities are likely to have a high Pathfinder score, making them ideal for partnerships that rely on modern, API-driven data exchange.
Targeting the underserved market: For smaller, rural hospitals, a different approach may be needed. Solutions that simplify data entry or use alternative exchange methods (like Direct Secure Messaging) may be more successful in these markets. This represents a potential new revenue stream for companies with flexible integration capabilities.
2. Building Your Product Roadmap: The indices highlight the shift from basic information exchange to advanced, API-based methods. This validates the importance of building your product on a modern, open API architecture. A strong Pathfinder score indicates a hospital is already on this path, which means less friction for your engineering teams and a faster path to go-live. A recent report by the American Medical Association (AMA) emphasizes that information blocking—a key component of the Friction Index—can be a result of technical limitations, not just malicious intent (AMA, 2024). This reinforces the need for digital health solutions that are flexible and standards-based to overcome these technical hurdles.
3. Navigating the Policy Landscape: The ONC developed these indices to track the impact of policies like the 21st Century Cures Act. The indices will be a key tool for policymakers to identify areas that need targeted intervention (Strawley & Everson, 2025). By understanding the Core, Pathfinder, and Friction scores, you can anticipate future regulations and align your company's mission with national priorities, such as improving patient access and addressing the digital divide.
Conclusion
The new ONC interoperability indices are more than just a measurement tool; they're a strategic resource. By analyzing the scores and their components, digital health companies can gain a competitive advantage by choosing the right markets, building the right technology, and positioning themselves as key partners in the ongoing journey toward true, nationwide interoperability.
References
American Medical Association. (2024, February 7). Proposed info-blocking rule is too harsh on physicians. Retrieved August 18, 2025, from https://www.ama-assn.org/practice-management/digital-health/proposed-info-blocking-rule-too-harsh-physicians
Strawley, C., & Everson, J. (2025, August 7). A new set of indices to measure hospital interoperability progress. Health IT Buzz. Retrieved August 18, 2025, from https://www.healthit.gov/buzz-blog/interoperability/a-new-set-of-indices-to-measure-hospital-interoperability-progress